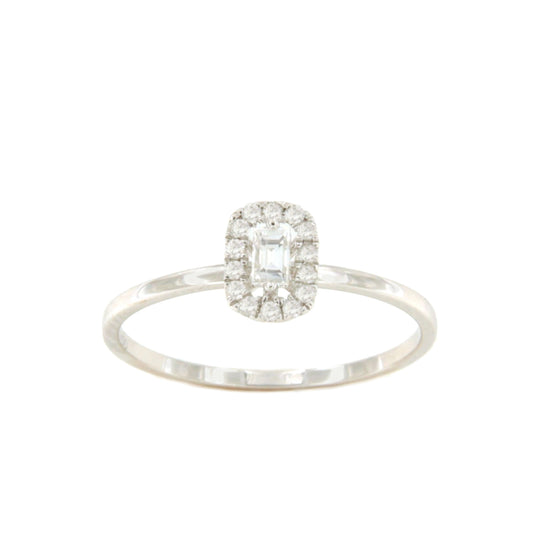
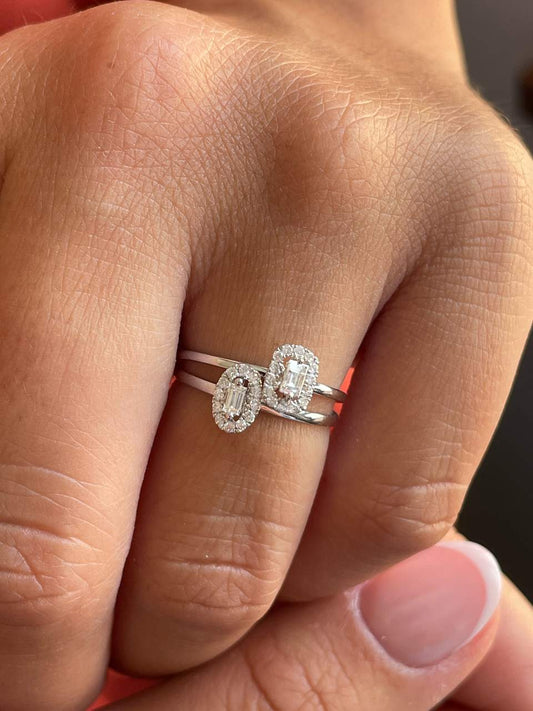
When choosing an engagement ring, countless questions arise to ensure you make the right choice. We will attempt to clearly explain some aspects to consider that will help you calculate the price of a diamond . This time, we will focus on the criteria for choosing rings set with brilliant-cut diamonds .
The 4Cs of Diamonds
The 4Cs are widely known when choosing a diamond; let's see what each one of them consists of.
1st CUT
This refers to the different cuts of the diamond : Brilliant or round, Pear, Oval, Baguette , Princess, Heart, Marquise,...
We developed the example using the most popular brilliant cut.
The carving or cutting process brings a lot of life to the stone. These techniques have evolved over time to optimize the result. We may have heard that a stone has an antique cut or a semi-cut when the crown or upper part is very closed or excessively open, depending on the number of facets.
Currently, the most commonly sold double-cut diamonds have between 57 and 58 facets. It is very important to know the diameter of the stone, as you might be sold a 0.50 ct stone that ideally should be around 5.1 mm.
Based on this criterion, the consumer should ask for the measurements of the stone's diameter.
Summary: Larger size and lower weight = Better choice as it will be appreciated as if it were a larger stone.

2ND COLOR
The color of a diamond is classified on a standardized chart. The color chart starts with the letter D for Diamond and goes up to Z.
- From D to F they are exceptional white
- From G to H they are white
- From I to J they are light in color
- From K to N they are colored

3rd CLARITY
It refers to the inclusions or imperfections that the stone has, that is, the purity of a diamond .
- IF = without any inclusion
- VVS1 = very, very small inclusion, only noticeable by an expert with a 10x magnifying glass
- VVS2 = very, very small inclusions, only noticeable by an expert
- VS1 = very small inclusion visible with a magnifying glass
- VS2 = very small inclusions visible with a magnifying glass
- SI1=small inclusions visible with a magnifying glass
- SI2 = small inclusions visible with a magnifying glass
It follows the scale 11,12,,13,… with greater inclusions.
The inclusions may appear in black, which are more visible, or in white, which are less noticeable.
4th CARAT (CARAT OR WEIGHT)
It is the main characteristic for determining the price of diamonds .
Diamonds are measured by their weight in carats with an equivalence of 1Ct = 0.20Gr
It is understandable that greater weight means a higher price, and in the stock market, prices tend to jump when they approach a multiple of 5 (e.g., 0.05-0.10-0.15...), and a big jump occurs when it goes from 0.50 Ct to 1.00 Ct or from 1.50 Ct to 2.00 Ct, and so on.
An example would be that a 0.95 Ct diamond can have a size of almost 1.00 Ct but a cheaper price.
Conclusion
It should be noted that the size (by weight e.g. 0.50Ct) of the stone we want to choose should have the largest possible diameter, that hardly any color is noticeable, that the inclusions are barely noticeable or none, and preferably white.